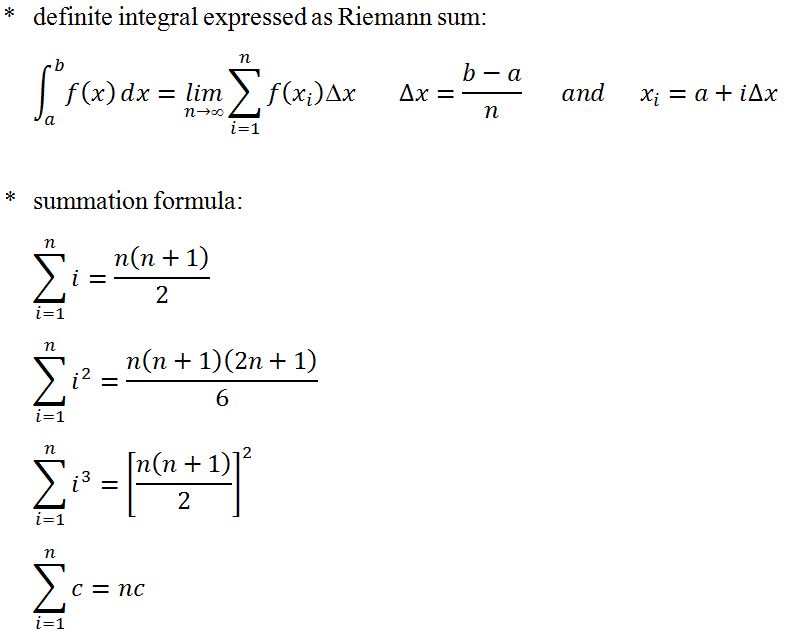
Riemann Sum: The Key to Mastering Area Under the Curve Explore Riemann sum, the foundation of integral calculus. Learn to break down complex areas into manageable rectangles, bridging basic geometry and advanced mathematics for real-world problem-solving.
Intros
0/4 watched
Examples
0/7 watched
- Finding the area under the graph of a function using a graphing calculator.
Consider the function , .
Find the area under the graph of using a graphing calculator. - Finding the area under the graph of a function using the Riemann Sum.
Consider the function , .
Estimate the area under the graph of using four approximating rectangles and taking the sample points to be: - Evaluating integrals with a Riemann Sum
Consider the function , . - Evaluating Riemann Sum with trapezoids
Consider the function , . Estimate the area under the graph of using four approximating trapezoids.






