Pythagorean identities
Everything You Need in One PlaceHomework problems? Exam preparation? Trying to grasp a concept or just brushing up the basics? Our extensive help & practice library have got you covered. | Learn and Practice With EaseOur proven video lessons ease you through problems quickly, and you get tonnes of friendly practice on questions that trip students up on tests and finals. | Instant and Unlimited HelpOur personalized learning platform enables you to instantly find the exact walkthrough to your specific type of question. Activate unlimited help now! |
Make math click 🤔 and get better grades! 💯Join for Free
Examples
Lessons
Free to Join!
Easily See Your Progress
 We track the progress you've made on a topic so you know what you've done. From the course view you can easily see what topics have what and the progress you've made on them. Fill the rings to completely master that section or mouse over the icon to see more details.
We track the progress you've made on a topic so you know what you've done. From the course view you can easily see what topics have what and the progress you've made on them. Fill the rings to completely master that section or mouse over the icon to see more details.Make Use of Our Learning Aids
Earn Achievements as You Learn
 Make the most of your time as you use StudyPug to help you achieve your goals. Earn fun little badges the more you watch, practice, and use our service.
Make the most of your time as you use StudyPug to help you achieve your goals. Earn fun little badges the more you watch, practice, and use our service.Create and Customize Your Avatar
 Play with our fun little avatar builder to create and customize your own avatar on StudyPug. Choose your face, eye colour, hair colour and style, and background. Unlock more options the more you use StudyPug.
Play with our fun little avatar builder to create and customize your own avatar on StudyPug. Choose your face, eye colour, hair colour and style, and background. Unlock more options the more you use StudyPug.
Topic Notes
What are the Pythagorean identities?
An identity in mathematics is an equation that is always true. The Pythagorean identities all involve the number 1 and its Pythagorean aspects can be clearly seen when proving the theorems on a unit circle.
Pythagorean identities
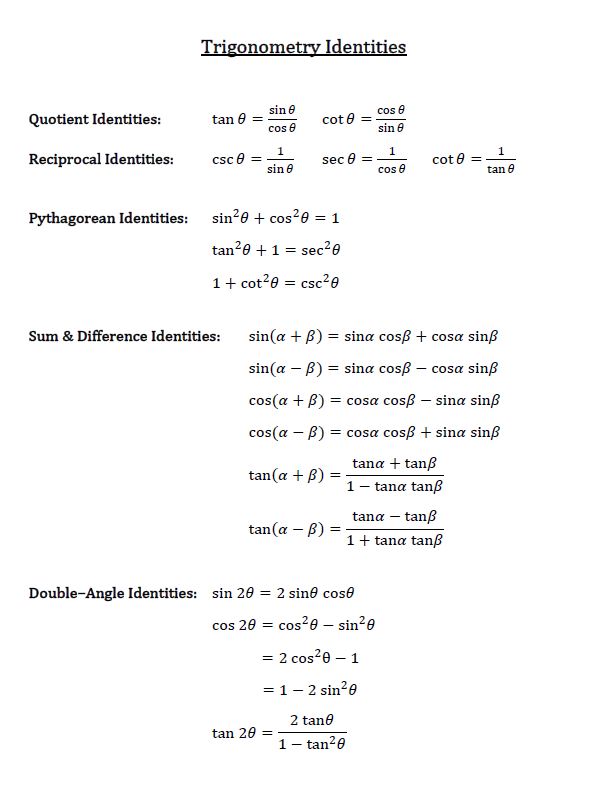
We are going to explore the Pythagorean identities in this question. You may refer to the below formula sheet when dealing with the 3 Pythagorean identities.
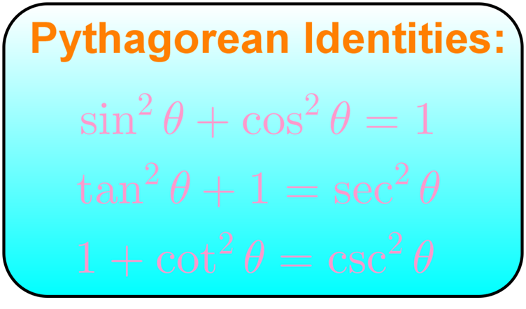
Let's explore the Pythagorean identities. The first of these three states that sine squared plus cosine squared equals one. The second one states that tangent squared plus one equals secant squared. For the last one, it states that one plus cotangent squared equals cosecant squared.
In the following question, we're going to try to use a unit circle to prove the first Pythagorean identity: sine squared plus cosine squared equals one.
Pythagorean identities examples
Question:
Use the unit circle to derive the Pythagorean Identity: cos2θ+sin2θ=1
How do we begin? Do you remember the properties of a unit circle? We've covered the unit circle in the previous section. To quickly recap, a unit circle is just a circle with radius of one unit, i.e. the radius must equal one.
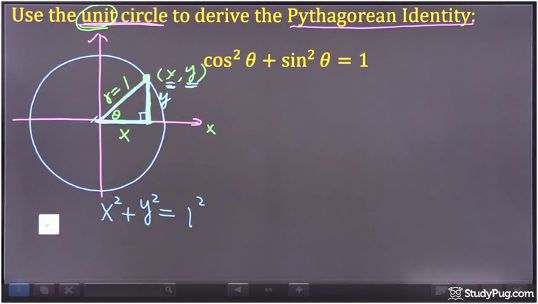
Refer to the above image. We'll identify a point on the circle at X,Y. Here, the X coordinate is X and the Y coordinate is Y.
From this point, let's draw a perpendicular line to the X axis. We will be focusing on this triangle.
In the above image, take a moment to recall what ? means. It's actually the reference angle, correct? It is one of the most important angles in trigonometry.
In the reference angle, what does it mean if the X coordinate equals X? It means that the length of the X segment is X. In a similar sense, if the Y coordinate is Y, that means the length of the vertical segment of the triangle would be Y.
Let's demonstrate this with actual numbers to illustrate that concept.
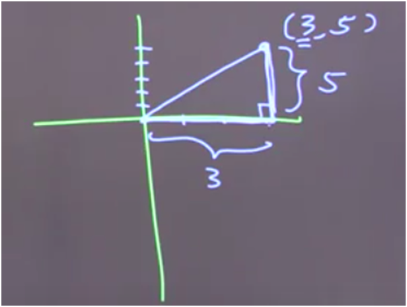
In the above example, there's a point called 3,5. If we draw a triangle, the 3 depicts the X coordinate. This means that the length of this segment is 3. Now, if the Y coordinate is 5, what does that mean? The length of the vertical segment in the triangle must be five.
Going back to the previous unit circle illustration, let's focus on the right-angled triangle and apply the Pythagoras theorem. What is the Pythagoras theorem? The Pythagoras tells us that X squared plus Y squared equals to the hypotenuse squared. The hypotenuse in this case is one, since we're using a unit circle. So here we have X squared plus Y squared equals one squared.
One neat thing about the unit circle is that its X coordinate can also be represented in terms of the angle theta. The X coordinate can be represented as cosine theta, while its Y coordinate can be represented as sine theta. Keep in mind that this is only for a unit circle. So for any point on the unit circle: the X coordinate can be represented as cosine theta; the Y coordinate can be represented as sine theta.

Through using the unit circle, the answer becomes very obvious. One squared is just one. The X coordinate can also be represented as cosine theta. The Y coordinate can be represented as sine theta. And voila! We are done. From the unit circle, we've successfully proved that cosine squared plus sine squared equals one, tackling one out of 3 Pythagorean identities.
Basic Concepts
Related Concepts
remaining today
remaining today



