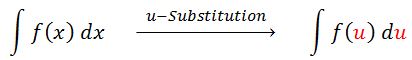hint: is usually the inside of a function, for example:
- the inside a power function:
- the inside a radical function:
- the inside of an exponential function:
- the inside of a logarithmic function: ?
- the inside of a trigonometric function:



U-Substitution is a powerful technique in calculus used for integrating complex functions. The introduction video provides a crucial foundation for understanding this concept, making it an essential starting point for students. U-Substitution, also known as substitution integration, involves replacing parts of the integrand with a new variable 'u' to simplify the integration process. This method is particularly useful when dealing with composite functions or expressions that involve products of functions and their derivatives. By strategically choosing a substitution, complex integrals can often be transformed into more manageable forms. U-Substitution is a fundamental tool in the integration toolkit, allowing mathematicians and students to solve a wide range of problems that would otherwise be challenging or impossible using basic integration techniques. Mastering U-Substitution opens doors to solving more advanced integration problems and is a crucial skill for anyone studying calculus or higher mathematics.
1. What is U-Substitution and why is it important in calculus?
U-Substitution is an integration technique used to simplify complex integrals by substituting a part of the integrand with a new variable, typically 'u'. It's important because it allows us to solve integrals that would be difficult or impossible using basic integration methods. This technique is particularly useful for integrals involving composite functions or products of functions and their derivatives.
2. How do I know when to use U-Substitution?
U-Substitution is typically appropriate when you notice a composite function in the integrand and its derivative (or part of it) appears as a factor. For example, in e^(2x) * 2dx, e^(2x) is a composite function, and its derivative (2e^(2x)) partially appears as the factor 2. This makes it a good candidate for U-Substitution.
3. What are common mistakes to avoid when using U-Substitution?
Common mistakes include choosing an inappropriate substitution, forgetting to change the limits of integration for definite integrals, omitting the du/dx term when substituting, and not including the constant of integration for indefinite integrals. Always double-check your work and verify your solution by differentiating the result.
4. Can U-Substitution be used for all types of integrals?
While U-Substitution is versatile, it's not suitable for all integrals. It works well for many polynomial, trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions, especially when they appear as composite functions. However, some integrals may require other techniques like integration by parts or trigonometric substitution.
5. How does U-Substitution relate to real-world applications?
U-Substitution has practical applications in various fields. In physics, it's used to calculate work done by variable forces. Engineers use it in fluid dynamics problems. Economists apply it to analyze consumer and producer surplus. Biologists use it in population growth models. These applications demonstrate how U-Substitution helps solve complex real-world problems across different disciplines.
Understanding U-Substitution in calculus requires a solid foundation in several key mathematical concepts. One of the most fundamental prerequisites is composite functions. These functions are essential because U-Substitution often involves recognizing and manipulating composite functions to simplify complex integrals.
Another crucial skill is determining trigonometric functions given their graphs. This ability helps in identifying suitable substitutions, especially when dealing with trigonometric integrals. Similarly, familiarity with the derivative of inverse trigonometric functions is vital, as these often appear in U-Substitution problems.
The derivative of logarithmic functions and understanding the natural log (ln) are also important. These concepts frequently arise in U-Substitution problems, particularly when dealing with exponential or logarithmic expressions. Likewise, knowledge of the derivative of exponential functions is essential for tackling a wide range of U-Substitution scenarios.
While it may seem unrelated at first, experience with solving 3 variable systems of equations by substitution can enhance your problem-solving skills and substitution techniques, which are directly applicable to U-Substitution in calculus.
Understanding the applications of polynomial functions provides context for many U-Substitution problems, as these often involve polynomial expressions. Additionally, the ability to determine the equation of a polynomial function can be helpful in recognizing suitable substitutions and in verifying your results.
Mastering these prerequisite topics will significantly enhance your ability to apply U-Substitution effectively. Each concept builds upon the others, creating a robust foundation for tackling complex integration problems. By understanding how these topics interconnect and relate to U-Substitution, you'll be better equipped to recognize patterns, choose appropriate substitutions, and solve a wide variety of calculus problems with confidence.