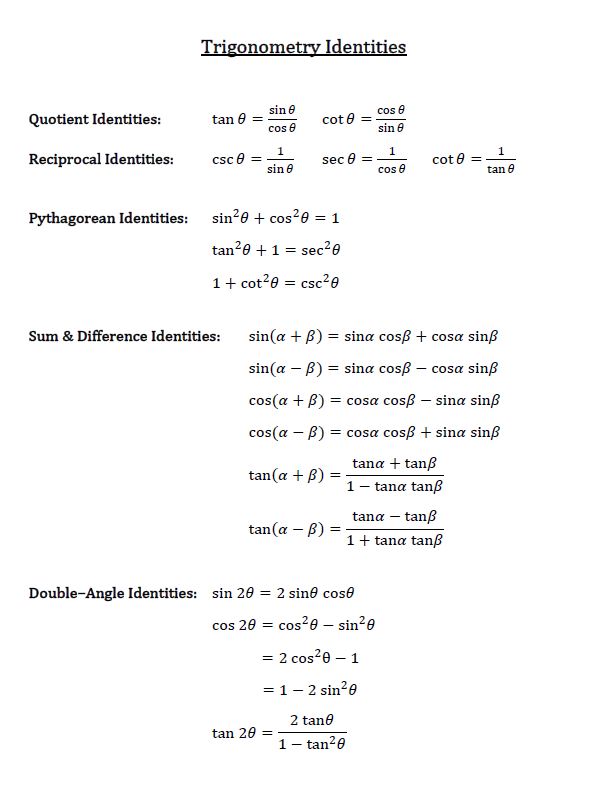
Sum and difference identities
All You Need in One PlaceEverything you need for better marks in primary, GCSE, and A-level classes. | Learn with ConfidenceWe’ve mastered the UK’s national curriculum so you can study with confidence. | Instant and Unlimited Help24/7 access to the best tips, walkthroughs, and practice questions. |