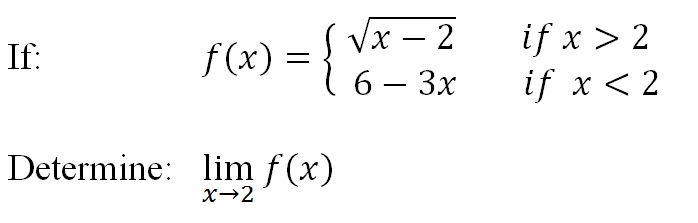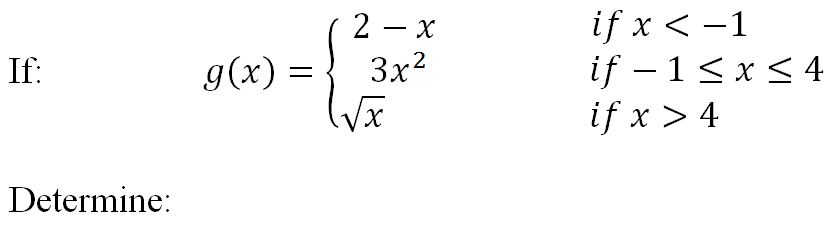Finding limits algebraically - direct substitution
Everything You Need in One PlaceHomework problems? Exam preparation? Trying to grasp a concept or just brushing up the basics? Our extensive help & practice library have got you covered. | Learn and Practice With EaseOur proven video lessons ease you through problems quickly, and you get tonnes of friendly practice on questions that trip students up on tests and finals. | Instant and Unlimited HelpOur personalized learning platform enables you to instantly find the exact walkthrough to your specific type of question. Activate unlimited help now! |